Fragments Microservices is a cloud-native microservice-based application designed to store, retrieve, and manage user-generated content (fragments) such as text, JSON, and binary data (e.g., images). The application is built using Node.js, Express.js, and deployed on AWS services for scalability and security.
The system allows users to perform basic CRUD operations on their fragments, with authentication and authorization handled via Amazon Cognito. Data is stored in AWS DynamoDB for metadata and Amazon S3 for binary content.
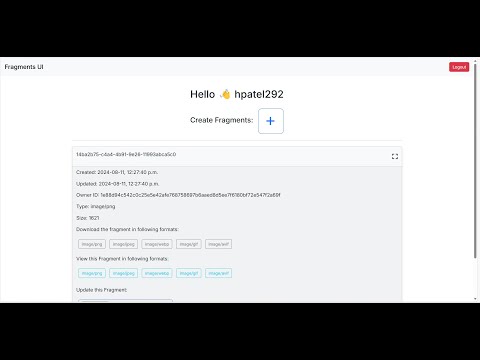
Watch the demo video of the Fragments Microservices project on YouTube:
- User Authentication & Authorization: Secured with Amazon Cognito to ensure only authenticated users can access the API.
- Fragment Management: Users can create, retrieve, update, and delete fragments (text, JSON, or images).
- Scalable Data Storage:
- Metadata is stored in AWS DynamoDB.
- Binary data is stored in Amazon S3.
- Microservices Architecture: The application is containerized using Docker and follows a microservices architecture for easy scalability.
- Logging and Monitoring: Integrated structured logging using Pino for efficient monitoring and error tracking.
- Automated Testing: Comprehensive unit and integration tests using Jest and Supertest.
- Backend: Node.js, Express.js
- Authentication: Amazon Cognito, Passport.js
- Database: Amazon DynamoDB (NoSQL)
- Storage: Amazon S3
- CI/CD & Containers: Docker, GitHub Actions, Docker Compose, LocalStack
- Testing: Jest, Supertest, Hurl
- Logging: Pino
- Cloud Infrastructure: AWS EC2, AWS Lambda, AWS SDK
- Version Control: Git, GitHub
To set up this project locally:
-
Clone the Repository:
git clone https://github.com/hpatel292-seneca/fragments-Microservices.git cd fragments-Microservices -
Install Dependencies:
npm install
-
Set Up Environment Variables:
Create a
.envfile in the root directory with the following variables:AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<your-access-key> AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<your-secret-key> AWS_REGION=<your-aws-region> S3_BUCKET_NAME=<your-s3-bucket-name> DYNAMODB_TABLE_NAME=<your-dynamodb-table-name> COGNITO_POOL_ID=<your-cognito-user-pool-id>
-
Run the Application:
npm start
-
Run Tests:
To run the test suite:
npm test
Once the application is up and running, you can access the API endpoints for managing fragments:
- Create Fragment:
- POST
/v1/fragments
- POST
- Get Fragment:
- GET
/v1/fragments/:id
- GET
- Update Fragment:
- PUT
/v1/fragments/:id
- PUT
- Delete Fragment:
- DELETE
/v1/fragments/:id
- DELETE
Refer to the Postman collection provided for detailed API usage.
- Base URL:
http://localhost:8080/v1/fragments - Authentication: The API uses Amazon Cognito tokens for authentication. Include the
Authorizationheader with a valid token for each request.
-
POST /fragments
- Create a new fragment (text, JSON, or binary data).
-
GET /fragments/:id
- Retrieve a specific fragment by its ID.
-
PUT /fragments/:id
- Update an existing fragment.
-
DELETE /fragments/:id
- Delete a fragment.
The project includes unit tests and integration tests to ensure code quality and functionality. You can run tests using:
npm testFor any inquiries or suggestions, feel free to reach out via:
- GitHub: hpatel292-seneca
- Email: [email protected]
This documentation is designed to provide an overview of your project, highlight the technologies used, and offer clear instructions on installation, usage, and contributing. Let me know if you need further customization!
npm start: Start the server.npm run lint: Lint code using ESLint on .js files stored under src folder.npm run dev: Start the server in development mode with debug logs enabled.npm run debug: Start the server in debug mode for remote debugging with a debugger attached.npm run test:watch: Runs Jest in watch mode with a specific configuration file.npm run test: Runs Jest tests with a specific configuration file.npm run coverage: Runs Jest to generate test coverage reports.
You can use tools like Postman or curl to interact with the API endpoints.