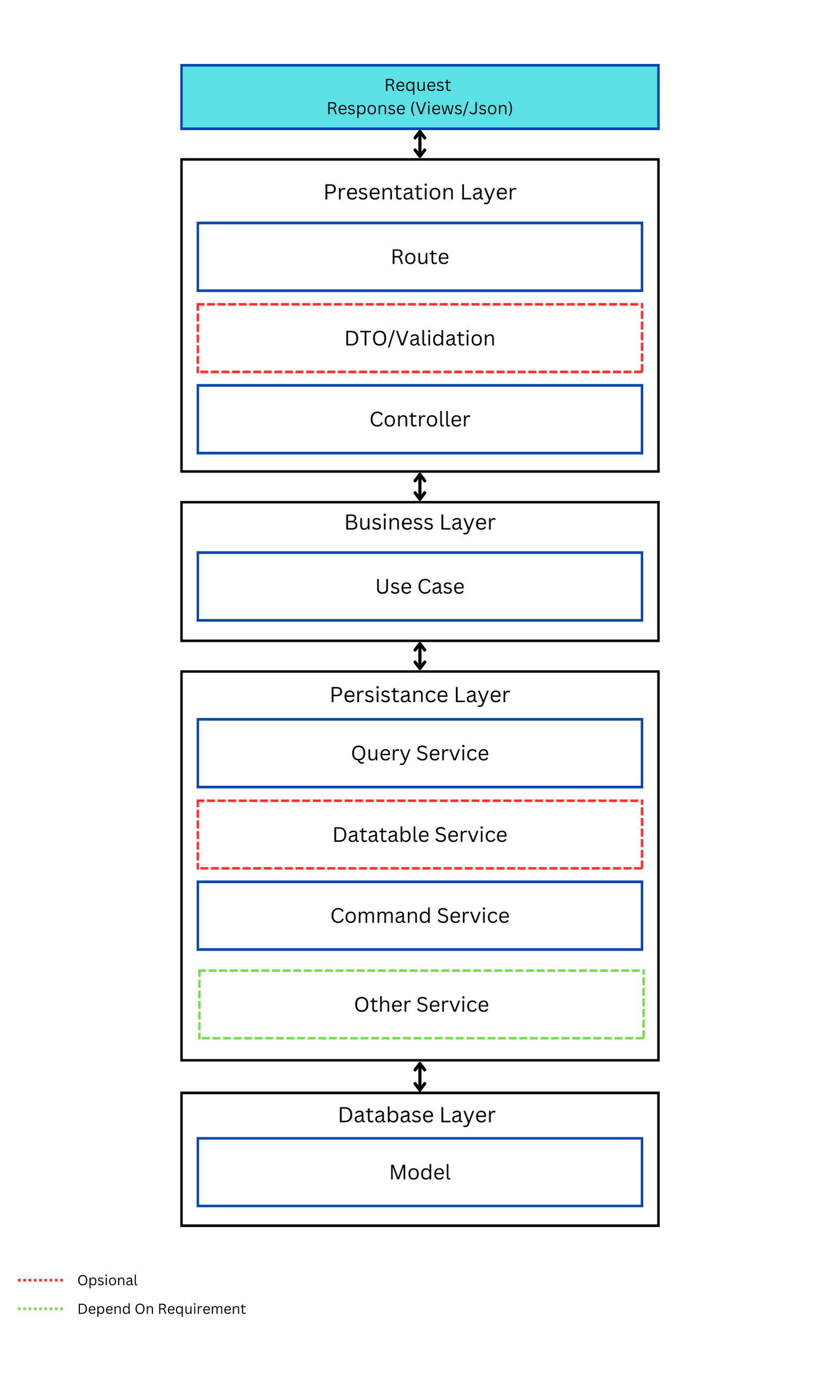
In the Laravel Framework, the standard uses an architecture, namely MVC (Model - View - Controller). This architecture is also included in the example of implementing the Layer Architecture, but there are obstacles that are encountered when we only implement MVC.
This problem is mainly encountered when we start developing a complex and continuous Laravel-based application, the MVC Architecture cannot handle it as a whole because all business logic is located only in the Controller. So if there is a change in the development team, the newly joined team will spend a lot of time studying the previous code.
One of the things that can be done to overcome is to develop from the standard Laravel Framework architecture to a more Clean Code architecture, but the problem is that there is no official standard for this and many novice programmers find it difficult to learn it.
With Laravel Layerize, you can separate the business logic from the Controller and organize your code into clear, separate layers. This package provides a ready-to-use directory structure and best practice approach to organize code according to their respective functions
The Laravel Layerize package has several layers namely:
- Presentation Layer: The layer closest to the user or the "presentation" of the application. Its main tasks include handling user interaction, such as receiving user input, displaying views, and sending responses to the user. Components in this layer include route, controllers, dto or form validation
- Business Layer: The layer that contains the business logic or business rules of the application. Its main tasks include orchestrating business processes, performing validation, making decisions, and processing data. This layer is technology-agnostic and responsible for keeping the business logic isolated from other implementation details. Components in this layer include use cases.
- Persistence Layer: The layer responsible for storing and retrieving data from persistent resources, such as databases or file storage. Its main tasks include performing CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on data. This layer provides an interface to access persistent resources and enables the application to store and retrieve data. Components in this layer include Command Service, Query Service, Datatable Service, and Other Service depend on requirements
- Database Layer: The layer that directly refers to the database system used by the application. It involves components such as the database server, database schema, tables, and queries. This layer serves as the infrastructure that supports the persistence layer in storing and retrieving data from the database.
By adopting a Laravel Layerize, applications can be well organized, have a clear structure, and separate responsibilities between each layer. This allows for easier maintenance, more structured development, and increases the scalability and flexibility of your application.
| Laravel Version | Support |
|---|---|
| 4.2.x | No |
| 5.x.x | No |
| 6.x.x | No |
| 7.x.x | Yes |
| 8.x.x | Yes |
| 9.x.x | Yes |
| 10.x.x | Yes |
- PHP Version "^7.3|7.4|^8.0|^8.1|^8.2"
- File (Default By Laravel Illuminate)
-
Open terminal, run this command
composer require deyan-ardi/laravel-layerize --dev -
After finish install, you can start use this package by run the command
-
Open terminal, run this command
composer update deyan-ardi/laravel-layerize
This package support folder generate, you can use "/" for create file in the folder (Ex: Admin/KonfigurasiController => to create class KonfigurasiController in Admin folder)
There are no changes to the route, you can implement the route according to the Laravel framework standards
DTO/Validation in Laravel Framework is handled by FormRequest. This package helps you create a FormRequest framework for you to validate on the user request side before going to the Controller. To create a FormRequest with Layerize, use the following command
php artisan layerize:dto User/StoreUserRequestThe result of the above command will give a class named StoreUserRequest which will be added to the App/Http/Requests/User folder
<?php
namespace App\Http\Requests\User;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Http\FormRequest;
class StoreUserRequest extends FormRequest
{
// Dto/validation with example implementation
public function authorize()
{
return true;
}
public function rules()
{
return [
// Validation rules
];
}
protected function prepareForValidation()
{
$this->merge([
// prepare for validation
]);
}
public function messages()
{
return [
// custom message of validation
];
}
public function attributes()
{
return [
// custom attributes of validation
];
}
}This package helps you create a Controller framework for you to send requests to the next layer. To create a Controller with Layerize, use the following command
php artisan layerize:controller UserControllerThe result of the above command will give a class named UserController which will be added to the App/Http/Controllers folder
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Helpers\Json;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;
use Throwable;
class UserController extends Controller
{
// Controller code with example implementation
public function __construct(
// protected UserUseCase $userUseCase,
) {
}
public function index()
{
// Render from use case
// return $this->userUseCase->renderIndex();
}
public function datatable(Request $request)
{
try {
// Render from use case
// DB::beginTransaction();
// $datatable = $this->userUseCase->renderDatatable($request);
// DB::commit();
// return $datatable;
} catch (Throwable $th) {
// DB::rollBack();
// return Json::error($th->getMessage());
}
}
public function create()
{
// Render from use case
// return $this->userUseCase->renderCreate();
}
// StoreUserRequest can be generate using layerize:dto
public function store(StoreUserRequest $request)
{
try {
// Render from use case
// DB::beginTransaction();
// $this->userUseCase->execStore($request);
// DB::commit();
// return redirect()->back()->with('success', "Data Successfully Added");
} catch(Throwable $th) {
// DB::rollBack();
// return redirect()->back()->with('error', $th->getMessage());
}
}
public function edit(string $id)
{
// Render from use case
// return $this->userUseCase->renderEdit($id);
}
// UpdateUserRequest can be generate using layerize:dto
public function update(UpdateUserRequest $request, string $id)
{
try {
// Render from use case
// DB::beginTransaction();
// $this->userUseCase->execUpdate($request, $id);
// DB::commit();
// return redirect()->back()->with('success', "Data Successfully Updated");
} catch(Throwable $th) {
// DB::rollBack();
// return redirect()->back()->with('error', $th->getMessage());
}
}
public function delete(string $id)
{
try {
// Render from use case
// DB::beginTransaction();
// $this->userUseCase->execDelete($request);
// DB::commit();
// return redirect()->back()->with('success', "Data Successfully Delete");
} catch(Throwable $th) {
// DB::rollBack();
// return redirect()->back()->with('error', $th->getMessage());
}
}
}This package helps you create a UseCase framework for you to perform business logic on your application. To create a UseCase with Layerize, use the following command
php artisan layerize:usecase UserUseCaseThe result of the above command will give a class named UserUseCase which will be added to the App/Http/UseCase folder
<?php
namespace App\Http\UseCase;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class UserUseCase
{
// Use case code with example implementation
public function __construct(
// protected UserQuery $userQuery,
// protected UserCommand $userCommand,
// protected UserDatatable $userDatatable,
) {
}
public function renderIndex()
{
// render view index
// return view('index');
}
public function renderDatatable(Request $request)
{
// render datatable
// return $this->userDatatable->datatable($request);
}
public function renderCreate()
{
// render view create
// return view('create');
}
// StoreUserRequest can be generate using layerize:dto, but must same with request send by controller
public function execStore(StoreUserRequest $request)
{
// exec store data
// return $this->userCommand->store($request),
}
public function renderEdit(string $id)
{
// render view create
// $findId = $this->userQuery->firstOrFail(['id' => $id]);
// return view('edit', compact('findId'));
}
// UpdateUserRequest can be generate using layerize:dto, but must same with request send by controller
public function execUpdate(UpdateUserRequest $request, string $id)
{
// exec store data
// return $this->userCommand->update($request, $id),
}
public function execDelete(string $id)
{
// exec store data
// return $this->userCommand->delete($id),
}
}This package helps you framework all the default services for you to interact with the database layer. To make all services default with Layerize, use the following command
php artisan layerize:service UserPage/User --allThe result of the above command will give three class named UserQuery,UserCommand,UserDatatable which will be added to the App/Services/UserPage/User folder
UserQuery.php<?php namespace App\Services\UserPage\User; use App\Services\Service; class UserQuery extends Service { public function __construct() { // self::setModel(User::class); call your model class name to use general function list } // Other Query Service here public function getCustomQuery(string $id) { // Other code here if query not support in getByAttr method } }
UserCommand.php<?php namespace App\Services\UserPage\User; use App\Services\Service; class UserCommand extends Service { // Command Service here // StoreUserRequest can be generate by layerize:dto, but must same with request send by UseCase public function store(StoreUserRequest $request) { // Code for store data } // UpdateUserRequest can be generate by layerize:dto, but must same with request send by UseCase public function update(UpdateUserRequest $request, string $id) { // Code for update data } public function delete(string $id) { // Code for delete data } }
UserDatatable.php<?php namespace App\Services\UserPage\User; use App\Services\Service; class UserDatatable extends Service { // Datatable Service here public function datatable(Request $request) { // Datatable server side processing code here } }
This package helps you framework a services for you to interact with the database layer. To make a services default with Layerize, use the following command
php artisan layerize:service UserPage/ApiProvider The result of the above command will give a class named ApiProvider which will be added to the App/Services/UserPage folder
<?php
namespace App\Services\UserPage;
use App\Services\Service;
class ApiProvider extends Service
{
// Your custom service code here
}There are no changes to the model, you can implement the model according to the Laravel framework standards
By configuring the Query Service, we provide some simple custom functions that can be used in Use Case to speed up the process of querying the database
- Create Query Service
- Add Model name in __construction Query Service Class
...
class UserQuery extends Service
{
public function __construct()
{
self::setModel(User::class); // add like this
}
...
}- Call Query Service in Use Case
...
class UserUseCase
{
public function __construct(
protected UserQuery $userQuery
)
{
}
...
}- One Query Service only can integrate with One Model, you can make many Query Service instances of Service
-
Default parameters
firstOrFail($where = [], $with = [], $orderBy = null, $orderDirection = 'asc') -
Example usage
$this->userQuery->firstOrFail(['id' => 5],['role'],'created_at','desc')-
Default parameters
first($where = [], $with = [], $orderBy = null, $orderDirection = 'asc') -
Example usage
$this->userQuery->first(['id' => 5],['role'],'created_at','desc')-
Default parameters
get($where = [], $with = [], $orderBy = null, $orderDirection = 'asc') -
Example usage
$this->userQuery->get(['role_id' => 5],['role'],'created_at','desc')-
Default parameters
getCount($where = [], $with = [], $orderBy = null, $orderDirection = 'asc') -
Example usage
$this->userQuery->getCount(['role_id' => 5],['role'],'created_at','desc')-
Default parameters
paginate($perPage = 10, $where = [], $with = [], $orderBy = null, $orderDirection = 'asc') -
Example usage
$this->userQuery->paginate(15, ['role_id' => 5],['role'],'created_at','desc')-
Default parameters
pluck($column, $where = [], $with = [], $orderBy = null, $orderDirection = 'asc') -
Example usage
$this->userQuery->pluck("name", ['id' => 5],['role'],'created_at','desc')-
Default parameters
chunk($size, $callback, $where = [], $with = [], $orderBy = null, $orderDirection = 'asc') -
Example usage
$this->userQuery->chunk(1000, function ($items) {
foreach ($items as $item) {
// Lakukan sesuatu dengan setiap item
}
}, ['category' => 'books'], ['author'], 'title', 'desc');-
Default parameters
firstOrNew($where = [], $attributes = []) -
Example usage
$this->userQuery->firstOrNew(['email' => '[email protected]'], ['name' => 'John Doe'])- GanaDev Com
- Open Source, to contribution please read CONTRIBUTING.md
- v2.0.0
The Laravel Layerize is open-sourced software licensed under the MIT license.

