🚌 🚌 🚌 🚌 🚌 🚌 🚌
AdvaBus can be used to seamlessly integrate a Spring Boot application with a message bus implemented using SQS and SNS.
From from the AWS docs:
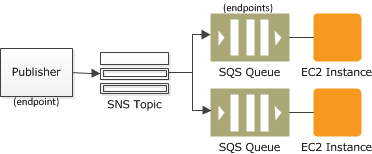
The "fanout" scenario is when an Amazon SNS message is sent to a topic and then replicated and pushed to multiple Amazon SQS queues, HTTP endpoints, or email addresses. This allows for parallel asynchronous processing. For example, you could develop an application that sends an Amazon SNS message to a topic whenever an order is placed for a product. Then, the Amazon SQS queues that are subscribed to that topic would receive identical notifications for the new order. The Amazon EC2 server instance attached to one of the queues could handle the processing or fulfillment of the order while the other server instance could be attached to a data warehouse for analysis of all orders received.
repositories { jcenter() }
dependencies {
compile 'com.advanon:advabus:0.2.0'
}AdvaBus assumes you have your AWS configuration already set. See the spring-cloud-aws
documentation for more details.
Add the queue name in your application.yaml:
message-bus:
queue: test-queueYou can also optionally specify a prefix for your topics, that will be combined with the topic name you will provide. This is useful, for example, for having different topics depending on the environment.
message-bus:
queue: test-queue
topics-prefix: test- For testing you may also want NOT to listen for incoming messages:
message-bus:
queue: test-queue
topics-prefix: test-
enabled: falseMessages are received from the queue as String, therefore they have to be converted to the actual desired type. To do so, you need an implementation of MessageBusConverter annotated with @MessageBusConverterService, to let AdvaBus know how to convert messages arrived from a specific topic:
@Service
@MessageBusConverterService("test-topic-name")
class UserMessageBusConverter(val mapper: ObjectMapper) : MessageBusConverter {
override fun convertMessagePayload(payload: String): User = mapper.readValue(payload)
}To receive the actual instance, just annotate a method of a service with @MessageListener, AdvaBus will figure out which message you're interested in based on the type of the argument.
@Service
class RandomService {
@MessageListener
fun onNewUser(user: User) {
println("RandomService: $user")
}
}You can define multiple listeners for the same argument type, AdvaBus will call all of them for each received message.
An instance of MessageBusPublisher can be injected in a service without any configuration:
@Service
class AnotherRandomService(private val publisher: MessageBusPublisher) {
fun sendMessage() {
publisher.publish("test-topic-name", User())
}
}AdvaBus uses a default implementation of ObjectMapper if no other one is available to serialize the messages to send.